XML Parsing in Android Using DOM
What
is an XML(Extensible Markup Language)?
Ans: XML stands
for Extensible Markup Language.XML was defined by W3C(World Wide Web
Consortium).
An XML document consists of elements, each element has a
start tag and an end tag,in between that content will be there.An XML file must
be "well-formed".An XML file is called valid if it is well-formed.
An Well-formed xml look like bellow:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<car>
<name>BMW</name>
<cost>2500000</cost>
</car>
XML Parsers in Android
Android
supports two types of XML Parsers:
1. DOM(Document
Object Model) Parser
2. SAX(Simple
API for XML) Parser
In this tutorial
we will see how DOM(Document Object Model) parsing hapenning in android. To
parse the xml file, we need xml data. So at first we will create a xml file,
then we will parse it in our android device.
To Create XML file, see bellow steps:
Go to your Notepad application, Type the following code:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<computers>
<brand>
<name>Apple</name>
<cost>45000</cost>
</brand>
<brand>
<name>Dell</name>
<cost>40000</cost>
</brand>
<brand>
<name>HP</name>
<cost>35000</cost>
</brand>
</computers>
Then go File->
Save as -> testxml.xml.
After generating this xml file, put this xml file Under assets
folder in your android project.See Bellow how it will look like:
Creating
Android Application Project for XML Parsing:
In Eclipse -> Create New Project(Named as
TestDomParser). -> Provide Activity Name(Here name as MainActivity). This
application building Android Version 4.2.2, API level 17.
MainActivity.java will look like this:
public class
MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void
onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
TextView tv_parse
=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
try{
InputStream
is = getAssets().open("testxml.xml");
DocumentBuilderFactory
dbFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder
dbBuilder = dbFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
Document
doc = dbBuilder.parse(is);
Element
element=doc.getDocumentElement();
element.normalize();
NodeList
nList = doc.getElementsByTagName("brand");
for (int i=0;
i<nList.getLength(); i++) {
Node
node = nList.item(i);
if
(node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element
elmnt = (Element) node;
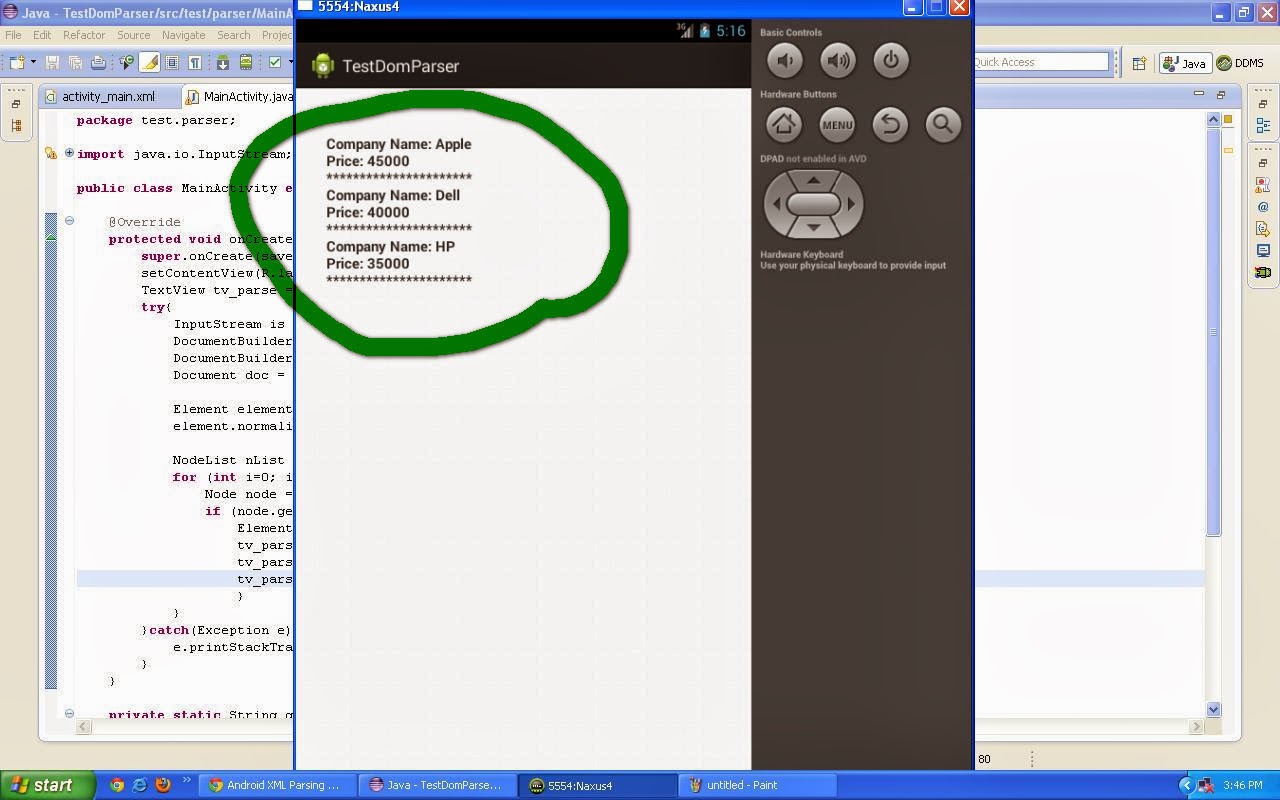
tv_parse.setText(tv_parse.getText()+"\nCompany
Name: " + getValue("name", elmnt)+"\n");
tv_parse.setText(tv_parse.getText()+"Price:
" + getValue("cost", elmnt)+"\n");
tv_parse.setText(tv_parse.getText()+"**********************");
}
}
}catch(Exception
e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static String
getValue(String tag, Element element) {
NodeList
nodeList = element.getElementsByTagName(tag).item(0).getChildNodes();
Node
node = (Node) nodeList.item(0);
return
node.getNodeValue();
}
}
Activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:textSize="15sp"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="14dp"
android:text="" />
</RelativeLayout>


No comments:
Post a Comment